MarkLogic 9 Product DocumentationAdministrator's Guide — Chapter 29
Understanding and Defining Schemas
This chapter describes schemas and lists procedures for defining them. The following topics are included:
For more information on the Schema database, loading schemas into MarkLogic Server, and using schemas in your applications, see the Loading Schemas chapter of the Application Developer's Guide.
Understanding Schemas
A schema is a data dictionary for your XML content. To specify a schema, you need to define the namespace to which the schema applies as well as the location of the schema file.
Schemas define the types of elements within XML documents. When knowing the type of an XML element would be beneficial to evaluating an XQuery program, MarkLogic Server will look for the relevant schema document (based on that element's namespace) using the following strategy:
- If the XQuery program explicitly references a schema for the namespace in question, MarkLogic Server uses this reference.
- Otherwise, MarkLogic Server searches the schema database for an XML schema document whose target namespace is the same as the namespace of the element that MarkLogic Server is trying to type.
- If no matching schema document is found in the database, MarkLogic Server looks in its
Configdirectory for a matching schema document. - If no matching schema document is found in the
Configdirectory, no schema is found.
Problems can arise in step 2 above when there are multiple schema documents in the schema database whose target namespace matches the namespace of the element that MarkLogic Server is trying to type. In this case, it is convenient to be able to use the Admin Interface to specify a default mapping.
Schema mappings can be specified for the HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC servers individually or for the group to apply to all HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC servers in the group. If the schema mapping defined for an HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC server conflicts with the schema mapping defined for the group, the former mapping is used.
When you specify a schema mapping in the Admin Interface, MarkLogic Server uses the following strategy to locate the schema:
- First, MarkLogic Server searches the schema database for a document with the exact URI you specified in the schema mapping.
If the schema mapping for the HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC server conflicts with the schema mapping for the group, the former mapping is used.
- If no matching schema document is found in the schema database, MarkLogic Server looks in its
Configdirectory for a schema document whose filename matches the filename portion of the URI you specified. - If no matching schema document is found in the
Configdirectory, no schema is found.
If a namespace is invoked by one or more data elements stored in a particular database, and the schema for that namespace is defined for the group or HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC server, MarkLogic Server applies the schema to the storage, indexing, and retrieval of that data.
The schema database in this case is the schema database for the database in which the data is located.
Procedures For Defining Schemas
Use the following procedures for defining schemas:
- Adding a Schema Definition for a Group
- Adding a Schema Definition for an HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC Server
- Viewing Schema Definitions for a Group
- Viewing Schema Definitions for an HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC Server
- Deleting a Schema Definition for a Group
- Deleting a Schema Definition for an HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC Server
Adding a Schema Definition for a Group
To make a schema available to all HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC servers in a group, complete the following procedure:
- Click the Groups icon on the left tree menu.
- Click the group in which you want to define the schema.
- Click the Schemas icon on the left tree menu, under the specified group.
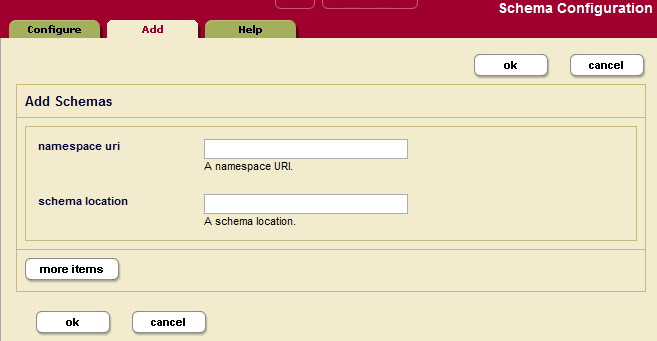
- Click the Add tab. The Schema Configuration page displays:
- Enter a namespace URI and corresponding schema location.
If you are planning to store the schema in your
Configdirectory, the following table lists the default location of theConfigdirectory on each platform:Platform Schema Directory Microsoft Windows C:\Program Files\MarkLogic\ConfigRed Hat Linux /opt/MarkLogic/ConfigMac OS X ~/Library/MarkLogic/Config/ - To add more schema definitions, click the More Items button and repeat step 5 for other schemas as needed.
- Scroll to the top or bottom and click OK.
Adding a Schema Definition for an HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC Server
To make a schema available to a particular HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC server, perform the following steps:
- Click the Groups icon on the left tree menu.
- Click the name of the group which contains the HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC server to which you want to add a schema.
- Click the App Servers icon.
- Click the name of the App Server to which you want to add a schema.
- Click the Schemas icon on the left tree menu, under the specified App Server.
- Click the Add tab. The Schema Configuration page displays:
- Enter a namespace URI and corresponding schema location.
If you are planning to store the schema in your config directory, refer to the following table for the default location of the config directory on your platform:
Platform Schema Directory Microsoft Windows C:\Program Files\MarkLogic\ConfigRed Hat Linux /opt/MarkLogic/ConfigMac OS X ~/Library/MarkLogic/Config/ - To add more schema definitions, click the More Items button and repeat step 7 for other schemas as needed.
- Scroll to the top or bottom and click OK.
Viewing Schema Definitions for a Group
To view a schema definition for a group, complete the following procedure:
- Click the Groups icon on the left tree menu.
- Click the group that contains the schema you want to view.
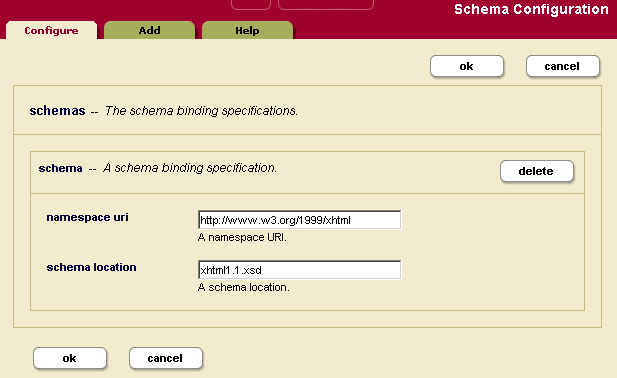
- Click the Schemas icon on the left tree menu, under the specified group.
The following example shows just one schema. It specifies that the schema for namespace http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml is found in the file xhtml.1.xsd, which is located in the config directory of your MarkLogic Server program directory.
Viewing Schema Definitions for an HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC Server
To view a schema definition for an HTTP or XDBC Server, perform the following steps:
- Click the Groups icon on the left tree menu.
- Click on the name of the group which contains the HTTP , ODBC, or XDBC server with the schema you want to view.
- Click the App Servers icon.
- Click the name of the App Server with the schema you want to view.
- Click the Schemas icon on the left tree menu, under the specified App Server.
The following example shows just one schema. It specifies that the schema for namespace http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml is found in the file xhtml.1.xsd, which is located in the config directory of your MarkLogic Server program directory.
Deleting a Schema Definition for a Group
To delete a schema definition for a group, perform the following steps:
- Click the Groups icon on the left tree menu.
- Click the group from which you want to delete the schema.
- Click the Schemas icon on the left tree menu, under the specified group.
- Locate the schema definition to be deleted from the system and click Delete.
- A confirmation message displays. Confirm the delete and click OK.
Deleting a Schema Definition for an HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC Server
To delete a schema definition for an HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC server, perform the following steps:
- Click the Groups icon on the left tree menu.
- Click the name of the group which contains the HTTP, ODBC, or XDBC server with the schema you want to delete.
- Click the App Servers icon.
- Click the name of the App Server with the schema you want to delete.
- Click the Schemas icon on the left tree menu, under the specified App Server.
- Click the Schemas icon on the left tree menu, under the specified App Server.
- Locate the schema definition to be deleted from the system and click Delete.
- A confirmation message displays. Confirm the delete and click OK.