MarkLogic 9 Product DocumentationMarkLogic Server on Microsoft® Azure® Guide — Chapter 1
Overview of MarkLogic Server on Azure
MarkLogic has partnered with Microsoft to deploy MarkLogic clusters on the Azure cloud with an officially supported MarkLogic Azure image, along with recommendations for your deployments. This guide covers the information and steps required to use MarkLogic on Azure. The solution template to configure the image can be found on Github [https://github.com/marklogic/cloud-enablement/]. In the Azure environment, you can deploy virtual machines (VMs) from the published MarkLogic Azure image. Or you can create MarkLogic clusters and resources including Load Balancers, Virtual Networks, and Virtual Machines using the Solution Template.
In addition to officially supporting MarkLogic on the Azure platform, many MarkLogic features are designed for better and easier deployment and management on cloud platforms. Features such as Encryption, Redaction, and Element Level Security enable MarkLogic to securely host your data in public cloud environments. For details about these features, see Encryption at Rest and Element Level Security in the Security Guide, and Redacting Content During Export or Copy Operations in the mlcp User Guide.
MarkLogic also includes telemetry, a support feature that aims to shorten resolution time by making system level log, metering, and configuration data accessible to MarkLogic Support. See Telemetry in the Monitoring MarkLogic Guide for more information.
This chapter includes the following sections:
- Azure Terminology
- Using MarkLogic Solution Template for Azure
- Deployment Options
- Typical Architecture
For more detailed information about Microsoft Azure, see the Microsoft Azure documentation.
Azure Terminology
Virtual Network is a representation of your own network in the cloud. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/virtual-networks-create-vnet-arm-cli for more information.
Availability Set is a logical grouping where virtual machines (VMs) created within an availability set are distributed across the underlying infrastructure. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/infrastructure-availability-sets-guidelines for details.
Public IP Address allows exposure of your content to the public Internet. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/virtual-network-deploy-static-pip-arm-cli for more information.
Managed Disks are the storage used to handle Azure Storage account creation and management in the background. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/convert-unmanaged-to-managed-disks for details.
Virtual Machines enable you to deploy a wide range of options for computing in an agile way. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/endorsed-distros for more information.
Using MarkLogic Solution Template for Azure
Using the Solution Template, you can customize various parameters for your MarkLogic cluster on Azure, such as Virtual Machine sizes and regions, specifying cluster names and admin credentials. The options for customization offered by the Solution Template are a subset of all of the configurable parameters for the resources associated with the cluster. The Solution Template is used to easily deploy one-node clusters or three-node clusters, using a developer's license or using your own existing MarkLogic license (known as BYOL or bring your own license).
The Solution Template makes it easy to deploy MarkLogic clusters and resources with customized parameters on the Azure platform. The Azure Resource Manager can also provide additional tools to manage the many resources available in a group.
Deployment Options
In the Azure environment, you can deploy virtual machines (VMs) from the published MarkLogic Azure image. You can then add the storage, networking, and security features that you require. You can use Solution Template to setup the IT environment via infrastructure as code concept.
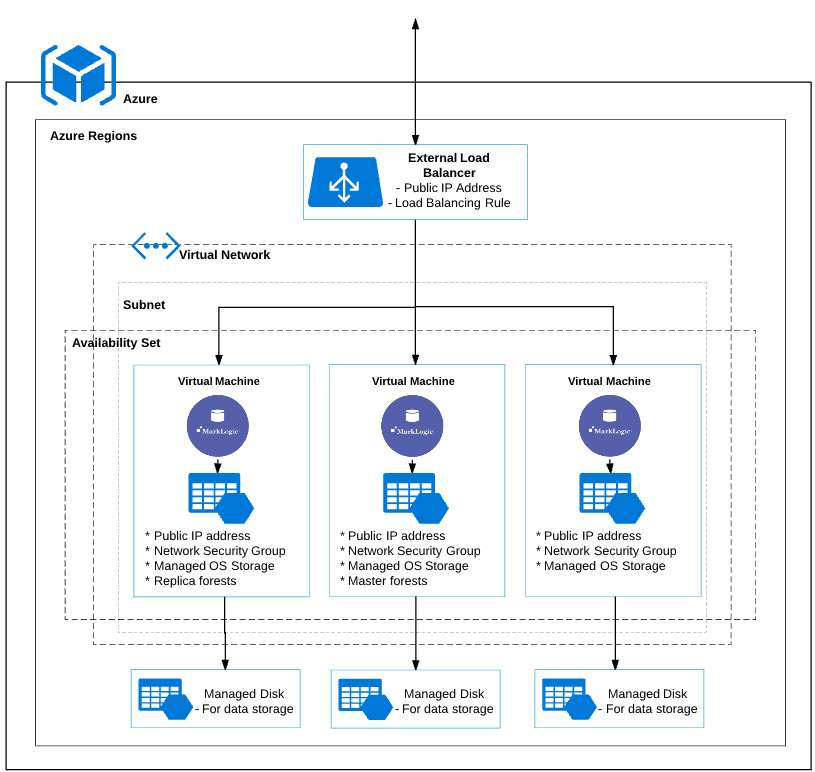
Typical Architecture
This diagram briefly explains the overall architecture of a cluster deployed on Azure.