MarkLogic 9 Product DocumentationMarkLogic Server on Microsoft® Azure® Guide — Chapter 2
Getting Started with MarkLogic Server on Azure
This chapter describes how to launch a MarkLogic Server cluster on Azure using the Solution Template to configure parameters. It includes additional information about supplying values for the template fields related to the cluster.
The parameter names used here are not a one-to-one mapping with Azure resource configurations.
This chapter includes the following sections:
- System Requirements and Installation
- Separate MarkLogic Converters
- Set up a Simple Deployment
- Resource Configuration
- Limitations
- List of Configurable Parameters
System Requirements and Installation
For a MarkLogic Azure image, you will need to choose a VM that has more than 2 GB of memory.
For production environment, Premium storage disks in Azure are preferred. Different VM instance types in Azure may support different storage types. See Requirements and Database Compatibility in the Installation Guide for information regarding MarkLogic requirements for Memory, Disk Space and Swap Space, and Transparent Huge Pages.
You will need this basic information to get set up. All of these are required:
- Subscription: Required by Azure. It is the Azure subscription to which the cluster usage will be billed.
- Resource Group: Required by Azure. The resource group to which the cluster will belong.
- Location: Required by Azure. Where you want to deploy the cluster.
- Deployment Name: Required. The value to be used as a prefix for all of your resources. There is a 10 character limit for the Deployment Name. Any blank spaces will be removed.
Important: You will need to setup your Azure account before proceeding to the next steps. After setting up the account, you can find your subscription ID under Subscriptions.
See Managing MarkLogic on Azure for more details about configuration options.
Separate MarkLogic Converters
Starting with MarkLogic 9.0-4, the MarkLogic converters/filters are offered as a package (called MarkLogic Converters package) separate from the MarkLogic Server package. For Azure, the converter installer/package is located in your default user home directory. There is a README.txt file in the package describing what the package is for, and pointing to the MarkLogic documentation for more information. See MarkLogic Converters Installation Changes Starting at Release 9.0-4 in the Installation Guide for more details.
Set up a Simple Deployment
This section covers the steps to set up at simple MarkLogic deployment. It is broken into these topics:
- Locate the MarkLogic Cluster Deployment Offering
- Configure Basic Settings
- MarkLogic Configuration
- Configure Cluster Resources
- Choose a VM Size
- Review the VM Summary
- Create and Purchase
Locate the MarkLogic Cluster Deployment Offering
The Azure Marketplace hosts the MarkLogic Cluster Deployment Offering online. With a browser, navigate to the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com/. Go to the Microsoft Azure Marketplace and search for MarkLogic.
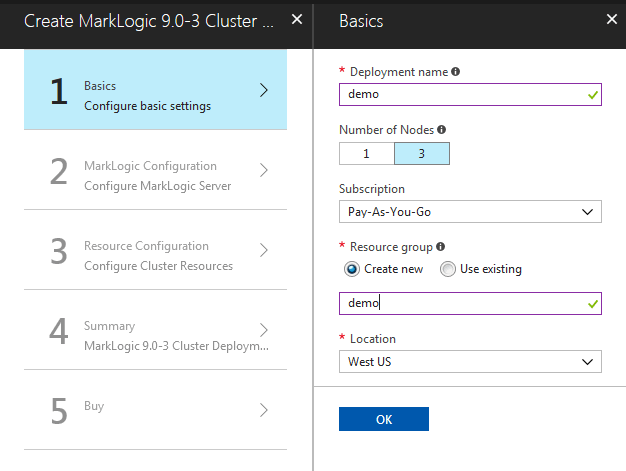
Configure Basic Settings
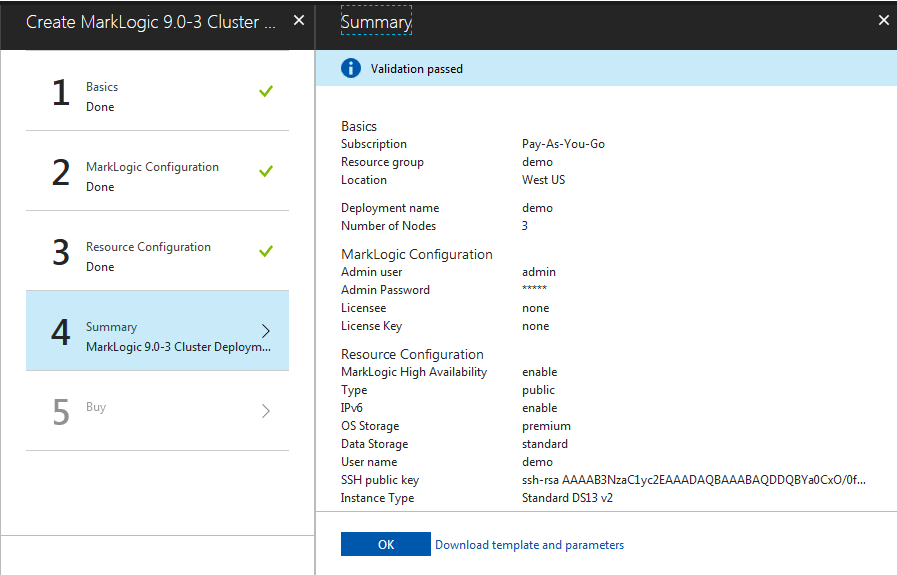
For these steps, you will enter the appropriate information for your cluster. The highlighted fields contain the default values. See the screenshots for details.
- Step one is to configure some basic settings like deployment name and number of nodes.
- The default field values that are highlighted can be changed. We recommend that you leave the defaults as is for this exercise. Click OK.
Each time you click OK, a validation program runs in the background to validate the entries in the fields. You cannot move to the next screen until the values have be validated. Validation is indicated by a green checkmark next to the step.
Basic Information Values
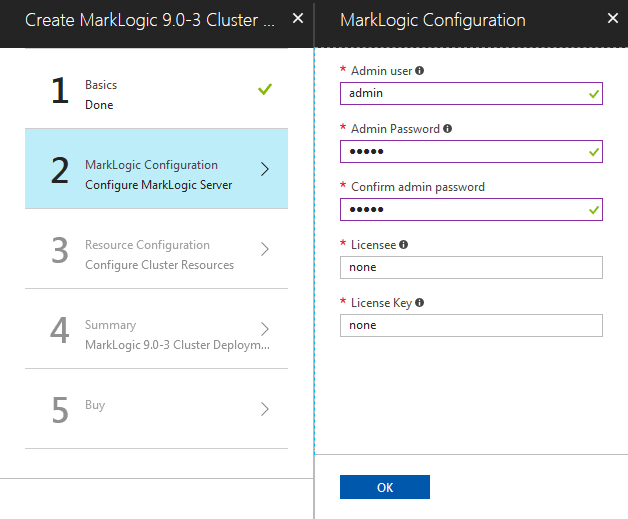
MarkLogic Configuration
- Fill in the fields for the MarkLogic Admin user and password, licensee, and license key. See the section on Password Policy for details on creating a password.
- Click OK.
Password Policy
Azure requires that when you use the MarkLogic Solution template to deploy MarkLogic on Azure, the admin password policy must be stronger than the default MarkLogic policy. Because of this, MarkLogic enforces a different admin password policy on Azure.
The regular expression to validate the policy is:
^(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[.!@#$%^&()-_=+])(?=.*[0-9])(?=.*[a-z]).{12,40}$ This means that your password must be 12-40 characters long and contain at least one uppercase letter, a digit, and a special character - one of .!@#$%^&()-_=+.
You can change your password later after the initial set up. When you change your password, the MarkLogic password policy will be used to validate the new password.
MarkLogic Configuration Values
When you provide a license key and a licensee, the template will deploy clusters using BYOL image.
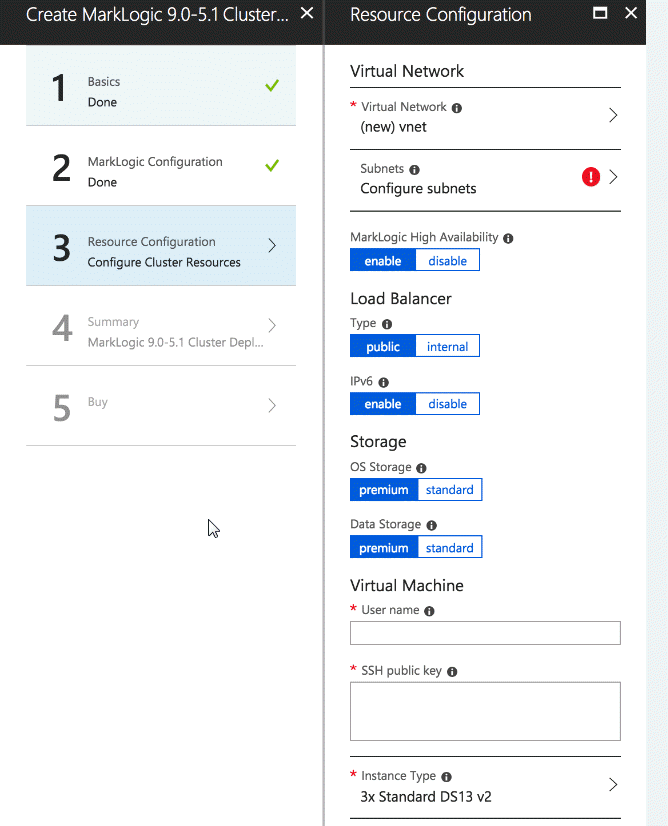
Configure Cluster Resources
- Configure your cluster resources. The default fields are highlighted.
- Click OK to continue. See Configure Cluster Resources Values for additional information.
Configure Cluster Resources Values
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| MarkLogic High Availability | enable or disable. Default is enable. This option is only applicable to a multi-node cluster. For a single node cluster, high availability will not be configured. When this option is set to enable, local disk failover will be configured for all database forests initialized with MarkLogic. Master forests will be configured on first node coming up in the clusters. The second node will be configured with replica forests. See Typical Architecture for an example of a forest topology. |
| Virtual Network | Virtual Network for MarkLogic cluster |
| Subnets | Subnets for MarkLogic. |
| Load Balancer: Type | public or internal. Default is Public Load Balancer |
| Load Balancer: IPv6 | enable or disable. Default is enable. IPv6 address on the load balancer. Only applicable if load balancer is public. |
| Storage: OS Storage | premium or standard. Default is premium. The storage type for the operating system of the virtual machines. |
| Storage: Data Storage | premium or standard. Default is premium. Storage type for data directory of virtual machines. |
| Virtual Machine: User name | Required. Operating system username for virtual machines. |
| Virtual Machine: SSH public key | Required. Public SSH key for the virtual machine listed. |
| Instance Type | Required. Type of virtual machine instance to launch. The list only includes instance types that meet the minimum standard requirements for MarkLogic Server. |
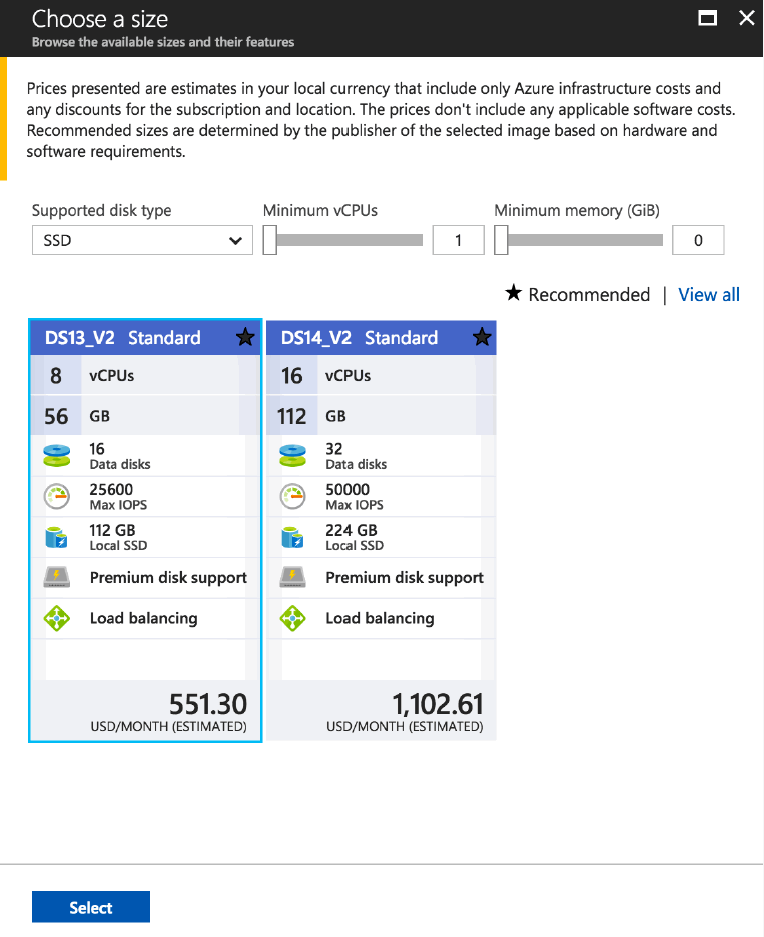
Choose a VM Size
All of the instance types displayed meet the minimum MarkLogic requirements. Other options have been filtered out for you. The choices will be displayed based on your prior selections.
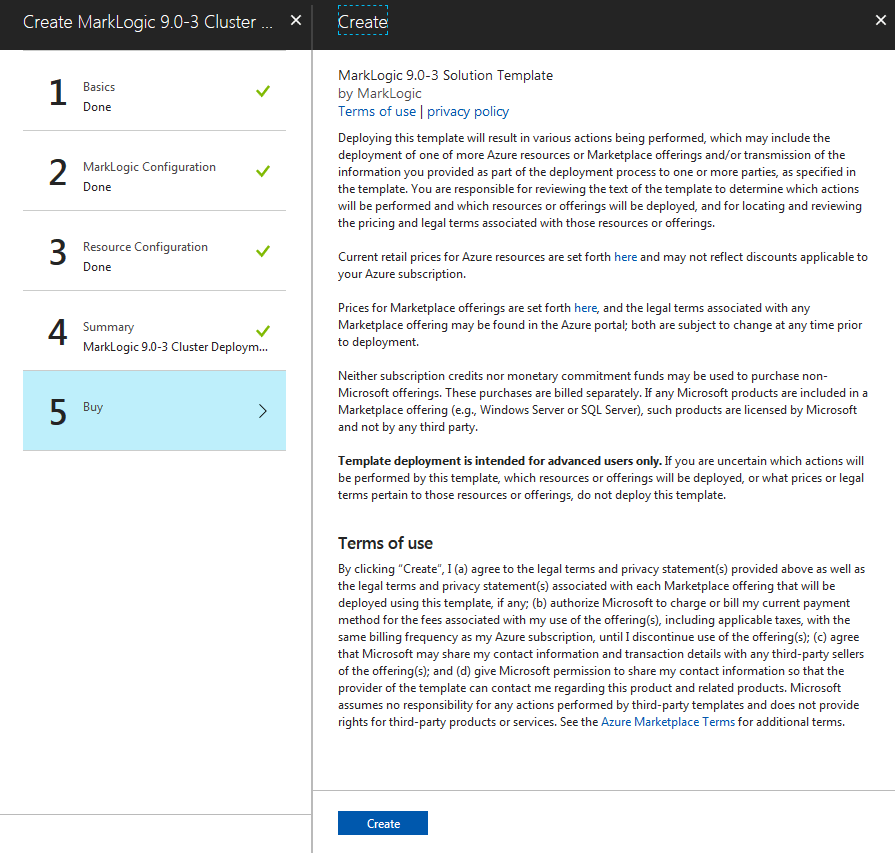
Create and Purchase
The next screen explains the terms of use and privacy policy. After reading the information and agreeing to these terms, click Create to create your MarkLogic cluster on Azure.
After you click create, the Azure VM will start up. The start up process can take a few minutes.
Resource Configuration
This section describes the configuration of cluster resources pre-defined in the template. These are fields that you fill in when you use the Solution Template to set up a cluster. These fields contain a subset of all of the configurable parameters for the resources associated with the cluster. The field names used in the Solution Template are not a one-to-one mapping of the Azure Resource configuration. In addition, for simplicity some of the configuration options are not included here (such as name of the VM instances, load balancer, availability set, and so on).
These topics are covered in this section:
- Virtual Network
- Availabilty Set
- Node Public IP Address
- Network Security Group
- Load Balancer
- Data Storage: Managed Disks
- Virtual Machines
- Cluster Initialization
Virtual Network
For the virtual network, specify the following information:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Address Space | 10.0.0.0/16 |
| Subnet Address Range | 10.0.1.0/24 |
Availabilty Set
Your VMs are placed into a logical grouping called an availability set. When VMs are created in an availability set, Azure distributes the placement of the VMs across the infrastructure. Availability Sets ensure that at least one VM remains running during planned or unplanned events.
See also Availability Set for about the limitations of Availability Sets.
Node Public IP Address
By default, Public IP addresses are dynamic, so they can change when the VM is deleted. To guarantee that a VM always uses the same public IP address, create a static Public IP.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Public IPv4 Allocation Method | Static |
| Public IPv6 Allocation Method | Dynamic |
| Idle Timeout (minutes) | 4 - Default value set by Azure |
Network Security Group
These are the applicable security rules for the cluster for allowed access, inbound.
| Usage/Name | Protocol | Source Port Range | Source Address Prefix | Destination Port Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSH | tcp | * | * | 22 |
| Admin | tcp | * | * | 8000-8010 |
| Health-Check | tcp | * | * | 7997 |
| Communication | tcp | * | * | 7778-7999 |
Load Balancer
It is a good practice to use a network load balancer between the client applications and a MarkLogic deployment. Depending on your deployment topology, you may use either an internet-facing load balancer or an internal load balancer.
An internet-facing load balancer should be used when a client application needs to access a MarkLogic deployment using public IP addresses. You should also consider network security in Azure for this type of deployment.
An internal load balancer should be used when the client application accesses a MarkLogic deployment using internal IP addresses, or the client application runs on premises and a secure VPN connection is established between the two networks.
The load balancer detects proper running of MarkLogic via the HealthCheck App Server on port 7997 and will only direct traffic to that node if it has verified that the MarkLogic instance is up. Therefore, for HTTP, the Load Balancer Probe in Azure for MarkLogic is on port 7997.
Public IP Address Allocation
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Public IPv4 Address Allocation Method | Static. Only applicable to public load balancer. |
| Public IPv6 Address Allocation Method | Dynamic. Only applicable to public load balancer. |
Load Balancing Rules
Data Storage: Managed Disks
Azure recommends using Managed Disks for your virtual machine data. Managed Disks handle storage for you behind the scenes, while providing better reliability for Availability Sets.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Create Option | Empty |
| Size (GiB) | 1023 |
Virtual Machines
Azure virtual machines enable you to deploy virtually any workload and any language on nearly any operating system.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Boot diagnostics | Enabled |
| Guest OS diagnostics | Disabled |
Cluster Initialization
The template will initialize all the cluster nodes with information provided by the user, and then start the cluster.
MarkLogic will mount the VM disk device /dev/sdc to the MarkLogic data directory.
On a multi-node cluster, if High Availability is enabled, the template will configure local-disk failover for forests initialized with MarkLogic Server in the cluster. The replica forests for App-Services, Documents, Extensions, Fab, Last-Login, Meters, Modules, Schemas, Security, and Triggers will be configured on a node other than the bootstrap node (the first node initialized in the cluster). The third node in a three node cluster, will have no forests at the start.
Limitations
This section includes limitations in Azure.
Availability Set
Azure Availability Set is a logical group for virtual machines. Microsoft Azure SLA guarantees that at least one of the (two or more) nodes in Availability Set is available 99.95% of the time. The Availability Set parameter is only applicable to a multi-node cluster. For a one-node cluster, the Availability Set parameter will be disabled.
See the Microsoft Azure SLA for your type of deployment for more information.
The configuration of an Availability Set includes the number of update domain and number of fault domain. The combination of the two domains can only guarantee that one of the nodes in Availability Set is available most of the time. You cannot configure an Availability Set that guarantees two of three nodes of a cluster will be available most of the time. For more information on Availability Set configuration, see the Azure documentation (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/manage-availability)
Shared Disk Failover
Users have the option to have High Availability (HA) configured for database forests initialized with MarkLogic. However only local disk failover is possible because Azure does not support mounting a managed disk for multiple machines. An alternative for managed disk is Azure File Storage - a shared storage service. The performance of the File Storage is not comparable to managed disk for mounting to virtual machines.
List of Configurable Parameters
The following tables contain fields from the set up example, for the configurable parameters in the MarkLogic Solutions template:
These topics are covered in this section:
Basic Information Values
Azure Configuration Values
Configure Cluster Resources Values
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| MarkLogic High Availability | enable or disable. Default is enable. This option is only applicable to a multi-node cluster. For a single node cluster, high availability will not be configured. When this option is set to enable, local disk failover will be configured for all database forests initialized with MarkLogic. Master forests will be configured on first node coming up in the clusters. The second node will be configured with replica forests. See Typical Architecture for an example of a forest topology. |
| Load Balancer: Type | public or internal. Default is Public Load Balancer |
| Load Balancer: IPv6 | enable or disable. Default is enable. IPv6 address on the load balancer. Only applicable if load balancer is public. |
| Storage: OS Storage | premium or standard. Default is premium. The storage type for the operating system of the virtual machines. |
| Storage: Data Storage | premium or standard. Default is premium. Storage type for data directory of virtual machines. |
| Virtual Machine: User name | Required. Operating system username for virtual machines. |
| Virtual Machine: SSH public key | Required. Public SSH key for the virtual machine listed. |
| Instance Type | Required. Type of virtual machine instance to launch. The list only includes instance types that meet the minimum standard requirements for MarkLogic Server. |