Query Console User Guide — Chapter 2
Query Console Walkthrough
This chapter provides a quick introduction to using the core Query Console features.
- Acessing Query Console
- Creating a Query
- Running a Query
- Changing the Query Output Format
- Using the Query Execution History
- Profiling a Query
- Exploring a Database
- Organizing Queries with Workspaces
Acessing Query Console
To begin using Query Console, open a browser and enter the URL:
http://your_host:8000/qconsole
If the application does not appear, you may not have sufficient privileges. To use Query Console, you must be a member of the qconsole-user role. If your privileges are insufficient, contact your MarkLogic Server administrator.
Query Console does not grant extra access to databases or documents. To perform operations such as document insertion or deletion or database exploration from Query Console, you must have appropriate security privileges.
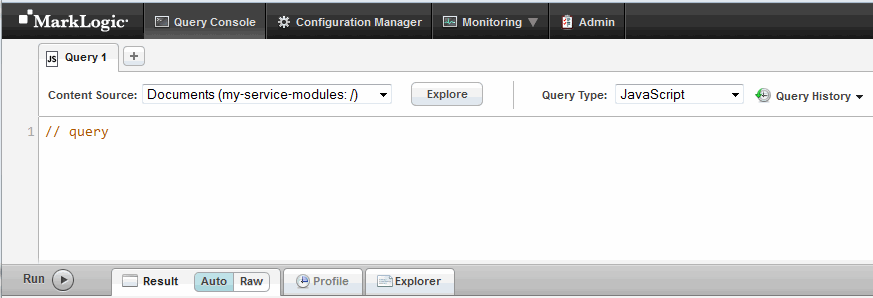
You should see a page similar to the following:
You should only have one Query Console session active at a time for any given MarkLogic user. Query Console saves state to MarkLogic Server. If a user has multiple Query Console sessions active concurrently, the state can become inconsistent. For example, do not log into Query Console as the same user in multiple browsers or browser tabs.
Creating a Query
This section walks you through creating a new query.
The following example assumes an empty workspace named Workspace, populated only with the default initial XQuery query, named Query 1. This is the configuration you see the first time you launch Query Console.
- If the current workspace is not Workspace, click on the workspace dropdown on the upper right and select the workspace named Workspace.
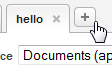
- Click on the "+" at the top of the query editor to the right of the open query tabs. A new query is created and opened in the editor. The new query also appears in the workspace panel on the right.
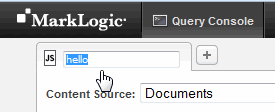
- Double-click on the query name in tab at the top of the editor and type in a meaningful name for the query, such as
hello. Notice the name changes in the tab and in the workspace panel on the right.You can also rename a query by double-clicking its name in the workspace panel.
- Choose the query type by clicking on the Query Type dropdown to the right of the Explore button. For this example, select XQuery.
The Query Type determines what query language MarkLogic Server assumes for you query when it is evaluated. The supported query langages are:
The following example shows a native SPARQL query with the Query Type set appropriately.
Running a Query
Follow this procedure to evaluate a query and view the results. You should already have entered your query in the query editor and selected the appropriate Query Type. If not, refer to Creating a Query.
- Click on the Content Source dropdown at the top of the editor to select a content source against which to run the query. For this example, you can use any content source.
- Click the Run button to evaluate the query. In this case, the default "hello world" query. The prettyprinted results display in the output pane at the bottom of the page.
- To view the query results as plain text, click the result format dropdown on the far right of the results pane and select Text. You query results display as plain text.
- To view the query results without prettyprint formatting, click the Raw button on the Result tab. Your raw query results display in the results pane at the bottom of the page. For details, see Changing the Query Output Format.
Changing the Query Output Format
Query Console supports two modes for displaying query results, Auto and Raw. The default mode is Auto. In Auto mode, your query results are formatted for readability based on the query and the output type. For example:
- XML and JSON query results are displayed with syntax coloring and UI elements that allow you to expand and collapse the element tree. Sequences are unrolled to line items with individual formatting controls.
- Results from a SQL query (run in SQL mode) are formatted as a table.
- Results from a SPARQL query display matching IRIs.
In Auto mode, you can override the default rendering using the format dropdown at the far right of the results pane.
For example, strings are rendered as text by default, but if you know the string contains serialized JSON, you can change the rendering to JSON to get syntax highlighting and tree controls. The choices on the format dropdown depend on the type of data returned by your query.
Raw mode always displays plain text, but it is not necessarily the query results exactly as returned from MarkLogic Server. Slight formatting changes are still applied to improve readability. For example, even in Raw mode, an XQuery sequence displays as line items rather than a comma separated list of values.
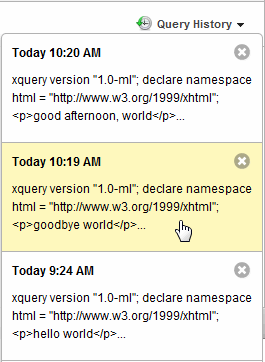
Using the Query Execution History
Each time you modify a query and evaluate it, Query Console saves the contents and time of execution in the Query History. Query Console maintains a separate history for each query.
Query Console adds a history entry for each unique version of a query. If the query text is unchanged between runs or if the changes create a duplicate of an existing history entry for the query, Query Console does not create a new entry.
Query Console saves at most 50 history entries.
- Click the Query History dropdown on the upper right. The history appears, with the most recent runs at the top of the list.
- To revert the query to a previous state, click on a history entry. The selected query version is restored in the editor.
To remove a history entry, click the delete (X) button in the upper right corner of the entry.
To close the history dropdown, click on the Query History dropdown again, or simply move the mouse outside the dropdown.
Profiling a Query
You can use Query Console to profile the performance of a query. Query Console profiles your query as if you passed your query to prof:invoke, and then displays a performance report in the results pane.
Profiling must be enabled on an App Server before you can profile a query. It is enabled by default when you create an App Server. For details, see MarkLogic Server Profiling Requirements Capabilities in the Query Performance and Tuning Guide.
Profiling is not available for Server-Side JavaScript queries.
- Click the Profile tab at the top of the result panel. The profile tab is brought to the front.
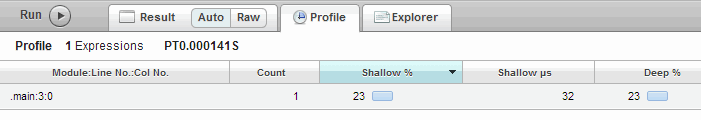
- Click the Run button to evaluate your query. A profiling report appears. If no profiling report appears, profiling may not be enabled for your App Server.
Your Query Console query appears as the
.mainmodule in the profiling report. - Click on a profiling report column header to sort the profiling data by a particular column. Each time you click a column, the order toggles between ascending and descending.
- Click on the Result tab to view the output from your query.
For details on profiling queries and the meaning of the profile report columns, see Profiling Requests to Evaluate Performance in Query Performance and Tuning Guide.
Exploring a Database
Use the Explore feature to browse the contents of a database. To explore a database:
- Select a database from the Content Source dropdown at the top of the current query.
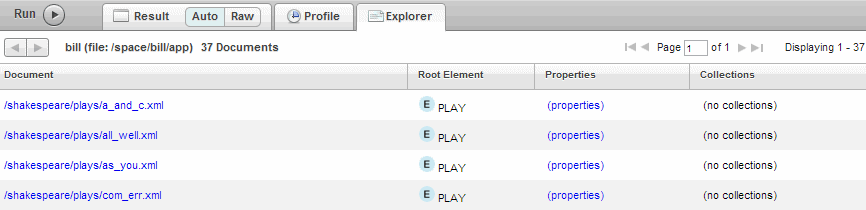
- Click Explore, to the right of the Content Source dropdown. Query Console displays a list of the documents in the selected database in the Explorer. For example:
For each document in the database, the summary includes the document URI, the type and name of the root node, a link to the document properties, and a link to any collections to which the document belongs.
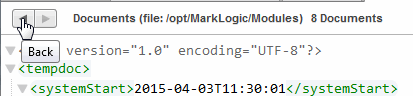
- Click on a document URI to view the document contents.
- Use the forward and back buttons in the upper left of the Explorer to navigate as you drill down into document contents, properties, and collections. For example, to return to the database content summary after clicking on a document's URI, click the back arrow.
- If there are properties associated with a document, click the link in the Properties properties column to view the properties as XML.
- If the document is part of a collection, click the collection name in the Collections column to explore that collection.
Organizing Queries with Workspaces
In Query Console, you organize your queries in workspaces. You can create multiple workspaces. However, only one workspace is active at a time. When you create a new query, Query Console automatically saves it in the active workspace.
- Workspace Overview
- Renaming a Workspace
- Copying a Workspace
- Deleting a Workspace
- Exporting a Workspace
- Importing a Workspace
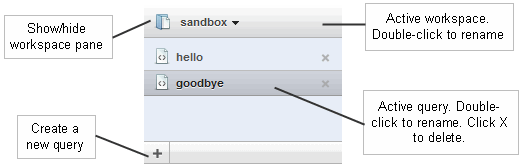
Workspace Overview
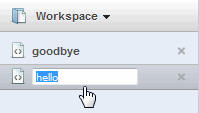
Use the workspace panel on the upper right of the page to interact with or change the active workspace. The workspace panel shows the name of the active workspace and lists the queries it contains:
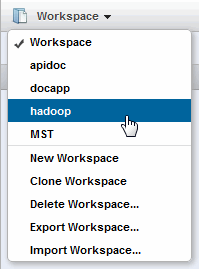
To see a list of available workspaces or to create, clone, delete, import or export a workspace, use the dropdown menu to the right of the workspace name:
Renaming a Workspace
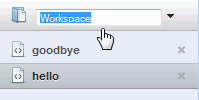
To rename a workspace, double-click on the workspace name at the top of the workspace panel:
Copying a Workspace
To create a new workspace that contains the same queries as an existing workspace:
- If the source workspace is not the active workspace, make it the active workspace by selecting it in the workspace menu.
- Click Clone Workspace in the workspace menu. A new workspace named "Clone of workspace_name" is created and becomes the active workspace.
- To rename the new workspace, double-click on the name at the top of the workspace panel.
When you clone a workspace, all the queries in the original workspace are copied to the new workspace. Query histories are not copied.
Deleting a Workspace
To delete a workspace and all of the queries it contains:
- If the workspace to delete is not the active workspace, make it the active workspace by selecting it in the workspace menu.
- Click Delete Workspace in the workspace menu.
- Click OK in the confirmation dialog box to confirm deletion of the workspace.
If you delete the last workspace, Query Console automatically creates a workspace with the default initial contents.
Exporting a Workspace
Export a workspace to share it with another user or use it on a different MarkLogic Server instance. Exporting a workspace saves the workspace and queries to an external file which can be imported back into Query Console. Query history is not exported.
Importing a Workspace
To import a previously exported workspace into Query Console:
- Click Import Workspace in the workspace menu. The "Import a Workspace" dialog box appears.
- In the dialog box, click the Choose File button to select an exported workspace XML file.
To cancel the import, click anywhere outside the dialog box.
- Click
Importto load the workspace. A loading progress window displays. - When loading completes, the imported workspace becomes the active workspace.
If a workspace already exists with same name as the imported workspace, the imported workspace name is modified by appending a unique number to the name.