Installation Guide for All Platforms — Chapter 2
Procedures
This section describes the following procedures to install MarkLogic on your system.
- Upgrading from Previous Releases
- Installing MarkLogic
- Starting MarkLogic Server
- Configuring the First and Subsequent Hosts
- Entering a License Key
- Checking for the Correct Software Version
- Configuring MarkLogic Server to Run as a Non-Daemon User
- Removing MarkLogic
Upgrading from Previous Releases
If you have previously installed MarkLogic on a machine, you must uninstall the old release before proceeding with the new installation. For information on removing the software, see Removing MarkLogic or the Installation Guide from the previous release. This section describes the following information and upgrade paths:
- Windows Service Parameters
- Upgrading from Release 9.0-1 or Later
- Upgrading from MarkLogic 7 or MarkLogic 8
- Upgrading from Release 6.0 or earlier
- Upgrading Clusters with DB Replication Configured
If you are upgrading a cluster to a new release, see Upgrading a Cluster to a New Maintenance Release of MarkLogic Server in the Scalability, Availability, and Failover Guide. The Security database and the Schemas database must be on the same host, and that host should be the first host you upgrade when upgrading a cluster.
MarkLogic Server does not support downgrades. Once you have upgraded to a later release, you cannot downgrade to your original release. To retain the option to restore to a previous version of MarkLogic Server, make a complete backup of your content and security databases before upgrading.
Windows Service Parameters
When upgrading MarkLogic on Windows as a different user from the user that installed the previous version, the MarkLogic service parameters in the Windows registry will be changed. When the old version of MarkLogic is uninstalled, the service is deleted from the registry, including any customizations to the service parameters. When the new version of MarkLogic is installed, the service is re-created in the registry, with the default service parameters.
Before starting the upgraded version of MarkLogic, make any customization to the service parameters. Otherwise the default service parameters will be set and MarkLogic will start up running as the local system user. Any MarkLogic configuration files saved as the local system user (such as those modified when making changes in the Admin Interface) will be created with the Windows file permissions for the local system user.
When you make changes the user in the service parameters, you should also change data directory file permissions because, if MarkLogic is running for any amount of time as the local system user, it is likely that is has written files as the local system user.
Upgrading from Release 9.0-1 or Later
To upgrade from release 9.0-1 or later to the current MarkLogic 11 release (for example, if you are installing a maintenance release of MarkLogic 11), perform the following basic steps:
- Stop MarkLogic Server (as described in step 1 of Removing MarkLogic).
- Uninstall the old MarkLogic 9 release (as described in Removing MarkLogic).
If you want to uninstall MarkLogic 9.0-4 or later, and if the converters package was previously installed with it, you will have to perform a two-step uninstall: first uninstall MarkLogic Converters and then uninstall MarkLogic Server. For more detail, see MarkLogic Converters Installation Changes Starting at Release 9.0-4 and Removing MarkLogic.
- Install the new MarkLogic 11 release (as described in Installing MarkLogic).
If you want to install MarkLogic 9.0-4 or later, and you plan to use the converters package with it, you will have to perform a two-step installation: first install MarkLogic Server and then install MarkLogic Converters. For more detail, see MarkLogic Converters Installation Changes Starting at Release 9.0-4 and Installing MarkLogic.
- Start MarkLogic Server (as described in Starting MarkLogic Server).
- Open the Admin Interface in a browser (http://localhost:8001/).
- When the Admin Interface prompts you to upgrade the databases and the configuration files, click the button to confirm the upgrade.
If you are upgrading a cluster to a new release, see Upgrading a Cluster to a New Maintenance Release of MarkLogic Server in the Scalability, Availability, and Failover Guide. The Security database and the Schemas database must be on the same host, and that host should be the first host you upgrade when upgrading a cluster.
If you are upgrading two clusters that make use of database replication to replicate the Security database on the master cluster, then you must enter the following to manually upgrade the Security database configuration files on the machine that hosts the replica Security database:
http://host:8001/security-upgrade-go.xqy?force=true
There is no direct upgrade path from Early Access releases of MarkLogic 11 to this release. If you need to move any data from an Early Access release to this release, you must re-create the data in the current release.
Upgrading from MarkLogic 7 or MarkLogic 8
MarkLogic 11 installs in the same default directory as earlier versions of MarkLogic, so there is no need to move any old files around. The upgrade to MarkLogic 11 does incorporate an automatic update to the Security database and to the configuration files. The Security database upgrade occurs when you first access the Admin Interface after the MarkLogic 11 installation.
When upgrading to MarkLogic 11, you must first uninstall previous releases of MarkLogic Server. Uninstalling a previous release of MarkLogic does not remove or delete the user data files (the forests and configuration information).
If you are upgrading a cluster of two or more servers, you must first upgrade the server in which the Security database is mounted. The Security database must be available before subsequent hosts can join the cluster.
The basic steps to upgrade from an earlier version to MarkLogic 11 are as follows:
- As a precaution, perform database backups on your earlier versions of MarkLogic Server databases.
- If you are upgrading from MarkLogic 7 and do not want to reindex a database, disable reindexing for that database before installing the new release (for example, set
reindexer enabletofalseon the Database Configuration page of the Admin Interface in MarkLogic 7). The entire database will be reindexed after upgrading to MarkLogic 11 unless you disable reindexing. For details, see Upgrades and Database Compatibility. You can always reindex the database later by settingreindexer enabledatabase configuration option totrue. - Stop MarkLogic Server (as described in step 1 of Removing MarkLogic).
- Uninstall the old MarkLogic release (as described in Removing MarkLogic).
- Install the new MarkLogic 11 release (as described in Installing MarkLogic).
If you want to install MarkLogic 9.0-4 or later, and you plan to use the converters package with it, you will have to perform a two-step installation: first install MarkLogic Server and then install MarkLogic Converters. For more detail, see MarkLogic Converters Installation Changes Starting at Release 9.0-4 and Installing MarkLogic.
- Start MarkLogic Server (as described in Starting MarkLogic Server).
- Open the Admin Interface in a browser (http://localhost:8001/).
- When the Admin Interface prompts you to upgrade the Security database and the configuration files, click the button to confirm the upgrade.
- If you have CPF installed in any database and you want to use any of the new pipelines in MarkLogic 11, then you must reinstall CPF for those databases. To reinstall CPF for a database, in the Admin Interface navigate to Databases -> database-name -> Content Processing, click the Install tab, and click the Reinstall button. This loads all of the new pipelines into the triggers database configured for that database.
There are some known application incompatibilities between MarkLogic 8 and MarkLogic 11, as well as some incompatibilities between MarkLogic 7 and MarkLogic 11. Some of the incompatibilities might require minor code changes to your applications. For details on these incompatibilities, see the Release Notes.
Upgrading from Release 6.0 or earlier
MarkLogic 11 only supports upgrading from Release 7.0 or later; it does not provide a direct upgrade path for previous releases of MarkLogic Server. If you are upgrading from a 6.0 or earlier release of MarkLogic Server, either install this release as a clean installation or upgrade your existing release to the latest Release 7.0 or 8.0 before installing this release. If you are upgrading from 6.0 and do not want to reindex your content, set the reindexer enable to false before upgrading. You can run MarkLogic 11 in either 7.0 or 8.0 compatibility mode, as described in Upgrades and Database Compatibility.
Upgrading Clusters with DB Replication Configured
If you are upgrading clusters with DB replication configured, see Upgrading Clusters Configured with Database Replication in the Database Replication Guide for details.
Installing MarkLogic
This section describes the procedure for installing MarkLogic Server on each platform. Perform the procedure corresponding to the platform to which you are installing.
| Platform | Perform the following: |
|---|---|
| Windows x64 |
|
| Red Hat Linux x64 |
|
| CentOS Linux |
|
|
|
| Amazon Linux 2 |
|
If you are installing MarkLogic 9.0-4 or later, and you plan to use the converters package, also perform the following steps:
|
|
| Mac OS X |
|
If you are upgrading a cluster to a new release, see Upgrading a Cluster to a New Maintenance Release of MarkLogic Server in the Scalability, Availability, and Failover Guide. The Security database and the Schemas database must be on the same host, and that host should be the first host you upgrade when upgrading a cluster.
It is not recommended to install the converters while MarkLogic Server is running. The reason for this is that the server checks the converters presence and version number only upon start-up. So the server will not have accurate information about the converters in this case. The recommended installation procedure is to stop the server if it is running, install or upgrade the server, install the converters, then start the server.
The following table shows the installation directory (<marklogic-dir>) and the default data directory for each platform:
The default forest directory is the same as the default data directory if the optional data directory is not specified during forest creation. On UNIX platforms, if you want MarkLogic Server to use another location for its default data directory, make your data directory (/var/opt/MarkLogic on Linux) a soft link to the alternate location.
In MarkLogic release 9.0-4 and later, MarkLogic Converters installation directory remains the same as in previous releases, namely:
| Platform | Converters Installation Directory |
|---|---|
| Windows | c:\Program Files\MarkLogic\Converters |
| Red Hat Linux | /opt/MarkLogic/Converters |
| Mac OS X | ~/Library/MarkLogic/Converters |
When a new node joins an existing cluster, the server does not try to figure out automatically whether the MarkLogic Converters package is needed or not. An XDMP-CVTNOTFOUND error will be thrown if converters/filters built-in functions are called on nodes that do not have MarkLogic Converters installed.
Starting MarkLogic Server
MarkLogic Server will automatically start when the computer reboots. To start MarkLogic Server without rebooting, perform the following command for the corresponding platform:
This starts all of the App Servers that are configured on your MarkLogic Server.
Verifying Converters Installation Starting at Release 9.0-4
In MarkLogic 9.0-4 or later, after starting MarkLogic Server, you may verify whether the converters package was installed with use of the XQuery API function xdmp:host-status or the JavaScript API function xdmp.hostStatus.
Suppose you want to verify whether converters are installed on a node with hostname englab.marklogic.com.
Open Query Console URL in a browser:
http://englab.marklogic.com:8000/qconsole/
Perform steps described in one of the following sub-sections, depending on your API of choice.
Obtaining Converters Version with XQuery API
In the Query Console, select XQuery as Query Type.
xquery version "1.0-ml"; xdmp:host-status(xdmp:host("englab.marklogic.com"))
In the response, look for the converters-version element, for example:
<converters-version>9.0-4</converters-version>
If converters are not installed, the above element will have an empty value.
Obtaining Converters Version with JavaScript API
In the Query Console, select JavaScript as Query Type.
'use strict'; xdmp.hostStatus(xdmp.host("englab.marklogic.com"))
In the response, look for the convertersVersion element, for example:
"convertersVersion" : "9.0-4"
If converters are not installed, the above element will have an empty string as its value.
Configuring the First and Subsequent Hosts
The following configuration procedures different depending on if you run MarkLogic Server in a cluster configuration or on a single host. The procedures are as follows:
- Configuring a Single Host or the First Host in a Cluster
- Configuring an Additional Host in a Cluster
- Leaving a Cluster and Becoming a Single Host
If you are configuring MarkLogic Server as a standalone host, or if this is the first host in a cluster configuration, follow the installation instructions in Section 2.4.1. Otherwise, follow the installation instructions in Section 2.4.2.
If you are upgrading a cluster to a new release, see Upgrading a Cluster to a New Maintenance Release of MarkLogic Server in the Scalability, Availability, and Failover Guide. The Security database and the Schemas database must be on the same host, and that host should be the first host you upgrade when upgrading a cluster.
Configuring a Single Host or the First Host in a Cluster
To configure this installation as a single host, or as the first host in a cluster, perform the following steps:
- Install MarkLogic and start MarkLogic as described in Installing MarkLogic and Starting MarkLogic Server.
- Log into the Admin Interface in a browser. It is on port 8001 of the host in which MarkLogic is running (for example, on the localhost,
http://localhost:8001). The Server Install page appears. - Click OK to continue.
- Wait for the server to restart.
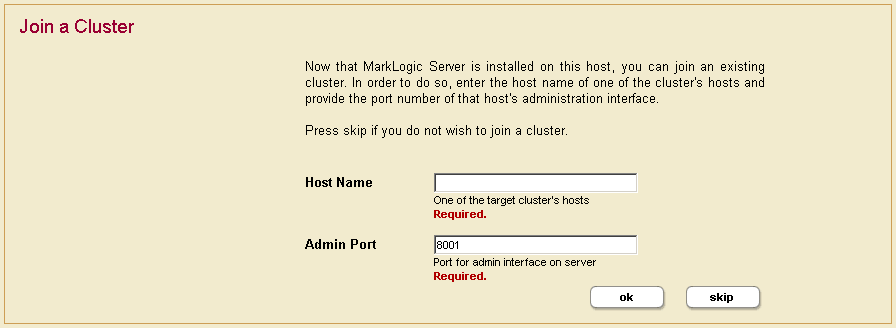
- After the server restarts, you will be prompted to join a cluster.
- Click Skip.
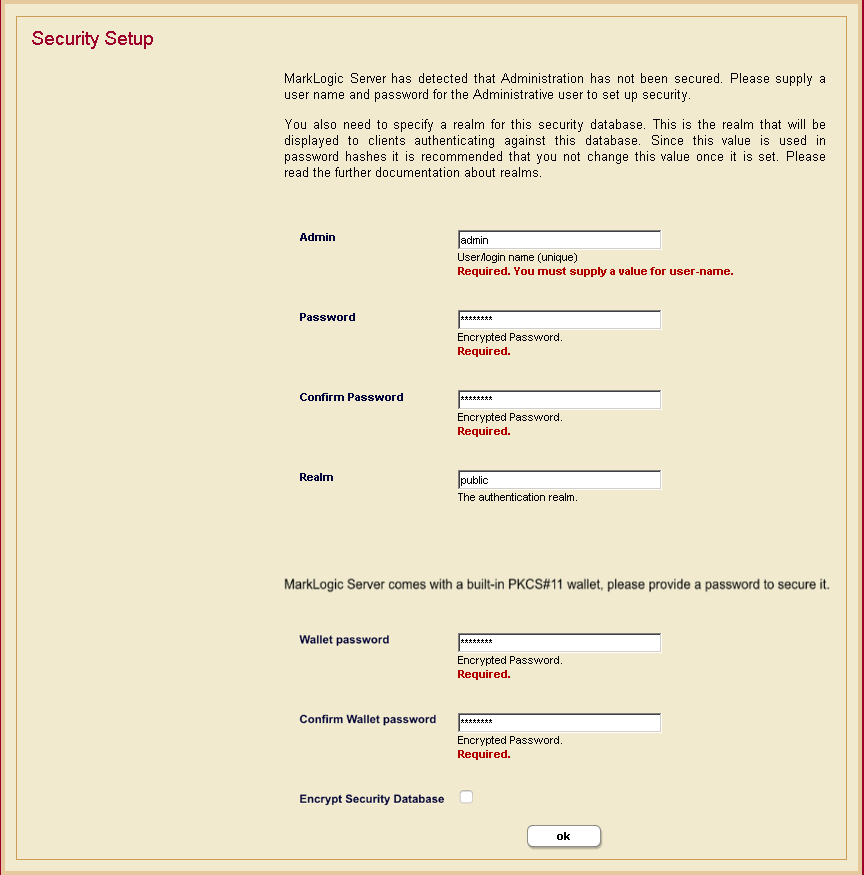
- You will be prompted to create an admin user and a PKCS#11 wallet password. Enter the login name and password for the admin user, and enter the wallet password.
- Click OK.
- You will be prompted to log in with your admin username and password.
You will now see the Admin Interface. If you do not need to add any hosts at this time, skip to Section 2.6.
Configuring an Additional Host in a Cluster
All hosts in a cluster have to be on the same platform. To configure this installation as an additional host in a cluster of the same platform, perform the following steps:
- On the node you want to add to an existing cluster, install MarkLogic and start MarkLogic, as described in Installing MarkLogic and Starting MarkLogic Server.
- Log into the Admin Interface in a browser. It is on port 8001 of the host in which MarkLogic is running (for example, on the localhost,
http://localhost:8001). The Server Install page appears. - Click OK to continue.
- Wait for the server to restart.
- After the server restarts, you will be prompted to join a cluster.
- Enter the DNS name or the IP address of one of the machines in the cluster. For instance, if this is the second host you are installing, you can enter the DNS name of the first host you installed.
- Click OK.
- You will be prompted for an admin username and password. You can use the admin username and password you created when installing the first host. Click OK.
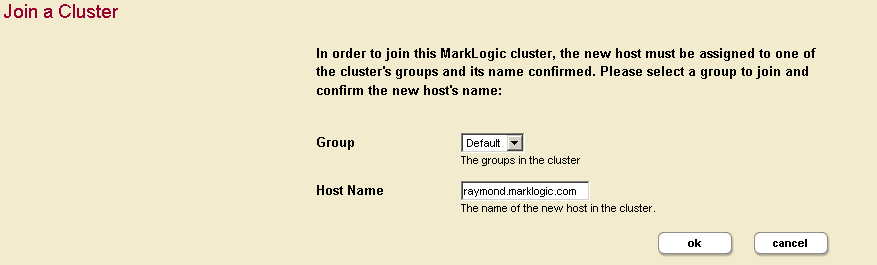
- Select a Group to assign this host. Click OK.
- Click OK to confirm that you are joining the cluster.
- You have now joined the cluster.
- Click OK to transfer the cluster configuration information.
You have completed the process to join a cluster and will now see the Admin Interface.
Leaving a Cluster and Becoming a Single Host
If your host is currently in a cluster of multiple hosts, and you would like to leave the cluster and switch to a single host environment, follow the steps in this section.
A host cannot leave a cluster if there are still forests assigned to it or if it has any foreign clusters associated with it. You must delete all forests assigned to the host and de-couple any clusters associated with a host before you can leave the cluster. However, you can delete the configuration only for a forest and the forest data will remain on the filesystem, allowing you to add the forest back to the host after changing the configuration. For instructions on adding a forest to a host, see the Administrator's Guide.
Perform the following steps to leave the cluster to which a host is connected:
- Run the Admin Interface from the host you want to remove from the cluster.
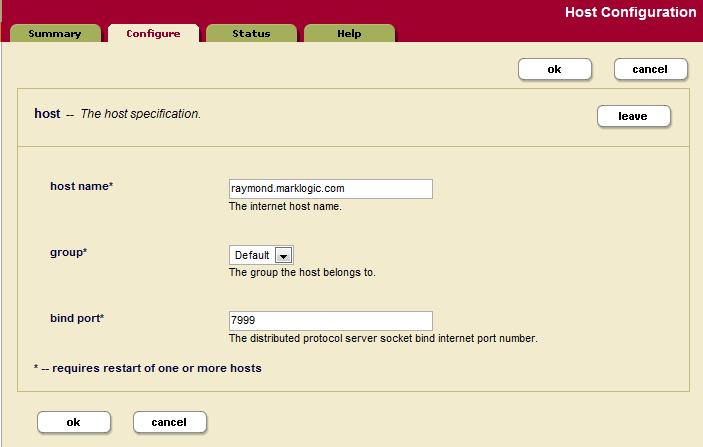
- Click the Hosts icon in the left menu tree. The Host Summary page appears.
- Click the name of the host you want to remove from the cluster, either from the left menu tree or from the Host Summary page. The Host Configuration page appears:
The Leave button only appears if the Admin Interface is running from this host.
- Click the Leave button
- Click OK to confirm leaving the cluster.
- The host restarts to load the new configuration.
- Follow the instructions in sections Configuring a Single Host or the First Host in a Cluster or Configuring an Additional Host in a Cluster as appropriate.
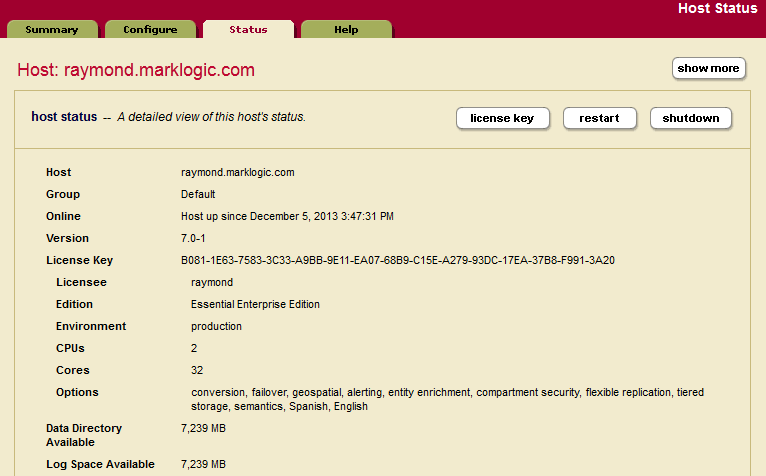
Entering a License Key
MarkLogic will run without a license key, but after installing MarkLogic you should enter a valid license key for the usage and features for which you are licensed. At any time, you can change the license key for a host from the Host Status page.
You might need to change the license key if your license key expires, if you need to use some features that are not covered in your existing license key, if you upgrade your hardware with more CPUs and/or more cores, if you need a license that covers a larger database, if you require different languages, or for various other reasons. Changing the license key sometimes results in an automatic restart of MarkLogic (for example, if your new license enables a new language).
To change the license key for a host, perform the following steps using the Admin Interface:
- Click the Hosts icon on the left tree menu.
- Click the name of the host for which you want to change the license key, either on the tree menu or the summary page. The Host Configuration page appears.
- Click the Status tab. The Host Status page appears.
- Click the License Key button. The License Key Entry page appears.
- Enter your new license key information. For information about licensing of MarkLogic Server, contact your MarkLogic sales representative.
- After entering valid information in the Licensee and License Key fields, click OK. If it needs to, MarkLogic will automatically restart, and the new license key will take effect.
Checking for the Correct Software Version
After logging in with your admin username and password, the Admin Interface appears. In the left corner of the Admin Interface, the version number and product edition are displayed.
To view more details about the release of MarkLogic Server that is installed and licensed, complete the following steps:
- Click the Hosts icon on the left tree menu.
- Select the name of the host you just installed, either from the left menu tree or from the Host Summary page.
- Click the Status tab. The Host Status page appears.
- Check that <version> is correct.
To begin using MarkLogic Server, see the following document:
Otherwise, you are finished with the Admin Interface for now. You have successfully installed MarkLogic on your system.
Configuring MarkLogic Server to Run as a Non-Daemon User
On UNIX-based systems (Linux), MarkLogic runs as the UNIX user named daemon. This section describes how to change a configuration to run as a different named UNIX user. This procedure must be run by the root user. Additionally, the root user is still required for installing and uninstalling MarkLogic and for starting and stopping MarkLogic from the startup scripts.
To modify an installation to run as a user other than daemon, perform the following steps:
- In a command window on the machine in which you installed MarkLogic, log in as the
rootuser. - Make sure MarkLogic is stopped. If it is still running, stop it as follows:
Platform Perform the following to stop MarkLogic: Red Hat Linux As the rootuser, enter the following command:/sbin/service MarkLogic stop
- Edit the configuration file for your platform using a text editor such as
vi.Platform Configuration File to Edit Red Hat Linux /etc/marklogic.conf
You must create the
/etc/marklogic.conffile if it does not exist. This file is only read by the MarkLogic startup; it is never written to; therefore, it will survive an uninstallation of MarkLogic. - In the file, edit the
MARKLOGIC_USERenvironment variable to point to the user in which you want MarkLogic Server to run. For example, if you want it to run as a user namedraymond, change the following line:export MARKLOGIC_USER=daemon
export MARKLOGIC_USER=raymond
- Save the changes to the
/etc/marklogic.conffile. - If you have not yet started MarkLogic after performing a clean installation (that is, after installing into a directory where MarkLogic has never been installed), then you are done and you can skip the rest of the steps in this procedure. If you have an existing installation (for example, if you are upgrading to a maintenance release), then continue with the following steps.
- For all of the MarkLogic files owned by
daemon, you need to change the owner to the new user. This includes all forest data and all of the configuration files. By default, the forest data is in the following directories:Platform Default Data Directory (for configuration and log files, and default forest directory) Red Hat Linux /var/opt/MarkLogicFor example, on a Linux system, perform a command similar to the following, which changes the owner to the user specified earlier in the
/etc/sysconfig/MarkLogicfile:chown -R raymond
/var/opt/MarkLogic - Make sure to change the owner for all forests in the system, otherwise forests will fail to mount upon startup. Note that the above command only changes the owner for forests installed in the default directory. You need to run a similar command on the data directory for each forest in which a data directory is specified.
- When you have completed all the file and directory ownership changes, start MarkLogic as described in Starting MarkLogic Server.
Once you have performed this procedure, all new files created by MarkLogic are created with the new user ownership; there will be no need to change any ownership again.
On Linux systems, use the /etc/marklogic.conf script to set environment variables. Any configuration changes you make to the MarkLogic-supplied startup script (for example, /etc/sysconfig/MarkLogic) will not survive an upgrade and need to be merged in during any upgrade of MarkLogic (because the installation installs a new version of the startup scripts). Under Linux, the unistallation process saves an old version of the scripts (for example, /etc/sysconfig/MarkLogic.rpmsave), so you can use that version to merge in your changes. If you perform a clean installation (not an upgrade installation), however, you will need to run this entire procedure again. If you use /etc/marklogic.conf for your environment variable changes, they will survive an upgrade and you will not need to merge your changes.
The following are default values of environment variables you can override in /etc/marklogic.conf on Linux-based systems (you will have to create the file if it does not exist):
export MARKLOGIC_INSTALL_DIR=/opt/MarkLogic export MARKLOGIC_DATA_DIR=/var/opt/MarkLogic export MARKLOGIC_FSTYPE=ext4 export MARKLOGIC_USER=daemon export MARKLOGIC_PID_FILE=/var/run/MarkLogic.pid export MARKLOGIC_UMASK=022 export MARKLOGIC_DISABLE_JVM=0 export MARKLOGIC_EC2_HOST export TZ=:/etc/localtime
Removing MarkLogic
To remove MarkLogic from your system, complete the following steps for the corresponding platform:
Using this procedure to remove MarkLogic from your system will not remove user data (configuration information, XQuery files used by HTTP or XDBC servers, or forest content). This data is left in place to simplify the software upgrade process. If you wish to remove the user data, you must do so manually using standard operating system commands.
In case you previously used converters/filters and want to remove this functionality:
- To remove MarkLogic Converters from a node that has MarkLogic 9.0-4 or later release installed, you can use package management tool, such as Control Panel on Windows or
rpmon Linux, to uninstall MarkLogic Converters. - To remove converters/filters from a node that has MarkLogic 9.0-3 or earlier release installed, you need to uninstall that release of MarkLogic, and then install MarkLogic Server from release 9.0-4 or later but do not install MarkLogic Converters.