MarkLogic Server 11.0 Product DocumentationSQL Data Modeling Guide — Chapter 5
Installing and Configuring the MarkLogic Server ODBC Driver
Tableau and other SQL tools require an ODBC driver on the client machine to communicate with MarkLogic Server. This chapter describes how to install and configure your MarkLogic Server ODBC driver on your client.
There is a 32-bit and 64-bit Windows MarkLogic ODBC driver and a 64-bit Linux ODBC driver, which are available from the MarkLogic Developer site:
http://developer.marklogic.com/products/odbc
Locate the ODBC driver for MarkLogic Server and follow the appropriate setup procedure to configure it on your client machine:
- Configuring the ODBC Driver on Windows
- Configuring the ODBC Driver on Linux
- Enabling Client Certificate Verification on an ODBC App Server
- Troubleshooting ODBC Driver Problems
Configuring the ODBC Driver on Windows
Tableau communicates with MarkLogic Server via a 32-bit or 64-bit ODBC driver. You must install and configure the ODBC driver that matches the word length (32 or 64-bit) of the connecting application, regardless of the MarkLogic server or operating system. For example, your computer may be running 64-bit windows with a 32-bit installation of Microsoft Excel. In this case, you will need the 32-bit ODBC driver to connect Excel to any MarkLogic instance. You can install the 32-bit and 64-bit ODBC drivers on the same machine.
This section describes how to configure your ODBC driver for use with MarkLogic.
- Launch the correct version of the Windows ODBC Data Source Administrator:
64-bit: %systemdrive%\Windows\System32\Odbcad32.exe 32-bit: %systemdrive%\Windows\SysWoW64\Odbcad32.exe
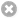
- Click the System DSN tab and click Add:
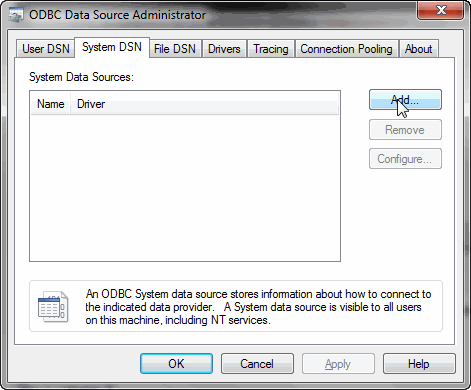
- Select either the
MarkLogic SQL(64-bit) orMarkLogic SQL (x86)(32-bit) driver and click Finish: - Set up an ODBC app server, as described in Create an ODBC App Server.
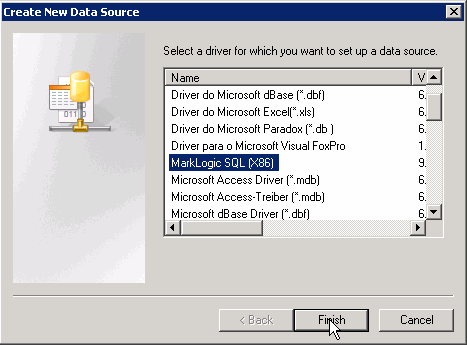
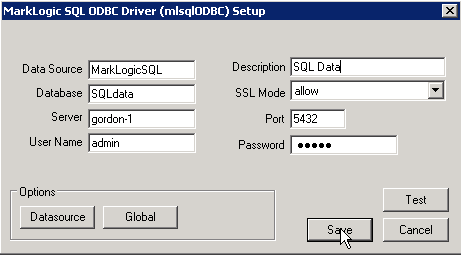
- In the MarkLogic SQL ODBC Driver Setup dialog, enter a name for your data source, the database name (SQLdata), the name of the machine that hosts your MarkLogic Server, the port number of your MarkLogic ODBC App Server (5432), set SSL mode to 'allow', and your MarkLogic Server login credentials. Click Test to test the connection to MarkLogic Server.
- If your connection test was successful, click Save. Otherwise, recheck your settings and retest.
Configuring the ODBC Driver on Linux
Dependencies:openssl and unixODBC.
The following procedure describes how to install the MarkLogic ODBC driver on Linux. The unixODBC tool is only needed for testing your connection to MarkLogic via the mlsqlodbc driver. If you don't think it is necessary to test your ODBC connection, then only do Step 3.
- Obtain a copy of unixODBC (used version
2.3.4in this example). You might be able to install it withyum, but if not, you can download the correct version from http://www.unixodbc.org/ to your/tmpdirectory and use the following procedure to install:cd /tmp tar -xvzf unixODBC-2.3.4.tar.gz cd /tmp/unixODBC-2.3.4 ./configure make sudo make install
- If you want to communicate with MarkLogic over SSL, you can install the openssl libraries as follows:
yum install openssl-libs
You can optionally install the GUI tools for unixODBC:
yum install unixODBC-gui-qt
- Install the ODBC driver package (named
mlsqlodbc-1.4-20170317.x86_64.rpmin this example):rpm -i mlsqlodbc-1.4-20170317.x86_64.rpm
- Call
odbcinstto write the DSN to the current user's.odbc.inifile:odbcinst -i -s -f /opt/MarkLogic/templates/mlsql.template
- The name of the ODBC driver is MarkLogicSQL. Use
isqlto connect to MarkLogicSQL to confirm that the ODBC driver was correctly installed (the MarkLogic username and password in this example is admin/admin):isql -v MarkLogicSQL admin admin
- If you don't want to have to enter your username and password each time you run
isql, you can edit the~/.odbc.inifile to add your MarkLogic username and password:[MarkLogicSQL] Description = MarkLogicSQL Driver = MarkLogicSQL Trace = No TraceFile = Database = marklogic Servername = localhost Username = admin Password = admin Port = 5432 Protocol = 7.4 ReadOnly = No SSLMode = disable UseServerSidePrepare = Yes ShowSystemTables = No ConnSettings =
- Test using
isqlwithout a username and password:isql -v MarkLogicSQL
If you encounter problems, make sure that the settings in the configuration files point to the right locations for your environment. Calling
odbcinst -jwill return the list of the configuration files for the ODBC driver.
Enabling Client Certificate Verification on an ODBC App Server
To enable client certificate verification for a MarkLogic ODBC App Server, you need a valid certificate/private key combination. Confirm that the ODBC App Server has a certificate template selected in the ssl certificate template field, has the appropriate certificate client authority selected in the ssl client certificate authorities field, and that ssl require client certificate is set to true.
To configure PostgreSQL for client certificate verification, point to the path of the certificate with the environment variable PGSSLCERT and the path of the private key with PGSSLKEY, as described in https://www.postgresql.org/docs/10/libpq-ssl.html#LIBPQ-SSL-CLIENTCERT.
For details on how to enable SSL for App Servers, see Configuring SSL on App Servers in the Security Guide.
Troubleshooting ODBC Driver Problems
This section describes how to log errors for debugging the ODBC driver.
Windows Troubleshooting
To turn on ODBC tracing on Windows:
- Launch the correct version of the Windows ODBC Data Source Administrator, as described in Configuring the ODBC Driver on Windows.
- Open to
Tracingtab - Click on the
Start Tracing Nowbutton and set the location of the log file inLog File Path. - Any error messages resulting from an ODBC API call are recorded in the log file.
To enable Mylog and CommLog on Windows:
- Launch the correct version of the Windows ODBC Data Source Administrator, as described in Configuring the ODBC Driver on Windows.
- Click the
System DSNtab and clickAdd. - Click on Add and select
MarkLogic SQLas the driver - Click the
Configurebutton. - Click the
Datasourcebutton. - Check the
Mylogbox. - Check the
CommLogbox.
Linux Troubleshooting
Locate the odbcinst.ini file. This file is commonly found in /etc/odbcinst.ini. If it is not there, locate it with odbcinst -j.
Edit the odbcinst.ini file and add the following to the top of the file:
[ODBC] Trace=Yes TraceFile=/tmp/odbctrace.log Debug=Yes DebugFile=/tmp/mylog.log
You can set TraceFile and DebugFile to any location of your choice.
For example, the traces should look like the following:
[ODBC][39034][1548446607.890671][__handles.c][460] Exit:[SQL_SUCCESS]| Environment = 0x55fa43ca2750 [ODBC][39034][1548446607.890736][SQLAllocHandle.c][375] Entry: Handle Type = 2 Input Handle = 0x55fa43ca2750 [ODBC][39034][1548446607.890798][SQLAllocHandle.c][493] Exit:[SQL_SUCCESS] Output Handle = 0x55fa43ca3050 [ODBC][39034][1548446607.890854][SQLConnect.c][3731] Entry: Connection = 0x55fa43ca3050 Server Name = [local-sql-els-odbc-7050][length = 23 (SQL_NTS)] User Name = [NULL] Authentication = [NULL] UNICODE Using encoding ASCII 'UTF-8' and UNICODE 'UCS-2LE' [ODBC][39034][1548446608.579017][SQLConnect.c][4309] Exit:[SQL_SUCCESS] [ODBC][39034][1548446608.579076][SQLGetFunctions.c][151] Entry: Connection = 0x55fa43ca3050 Id = SQLMoreResults Supported = 0x55fa438fc004 [ODBC][39034][1548446608.579098][SQLGetFunctions.c][186] Exit:[SQL_SUCCESS] Supported = 0x55fa438fc004 -> 1